Data Modeling with AQL
What is a data model
A data model is an abstract representation on top of a database table/SQL query that you may manipulate without directly affecting the underlying data.
from Holistics Documentation
This definition is a bottom-up definition. From a top-down point of view, a data model represents a Business Entity.
The fact that it's backed by a database table or a SQL Query is only an implementation detail. For example, every business has its own concept of What a User is. The job of a data model is to expose a concrete object representing that concept for Business Users to reason and interact with.

One crucial aspect of understanding the data model is understanding what Dimensions and Measures are.
Measure
Measures are numeric values obtained by aggregating individual values, serving as key indicators (KPIs) for specific aspects or processes of a business. Using the context of the user model as an example, a measure would be something like total_users, active_users, life_time_value, etc.
However, measures alone may lack meaning. How can we address questions about factors such as
- "What led to the growth in Total Users this month"?
- "Where did the new users come from?"
- "Was it a result of a recent promotion?"
This is where dimensions come in
Dimension
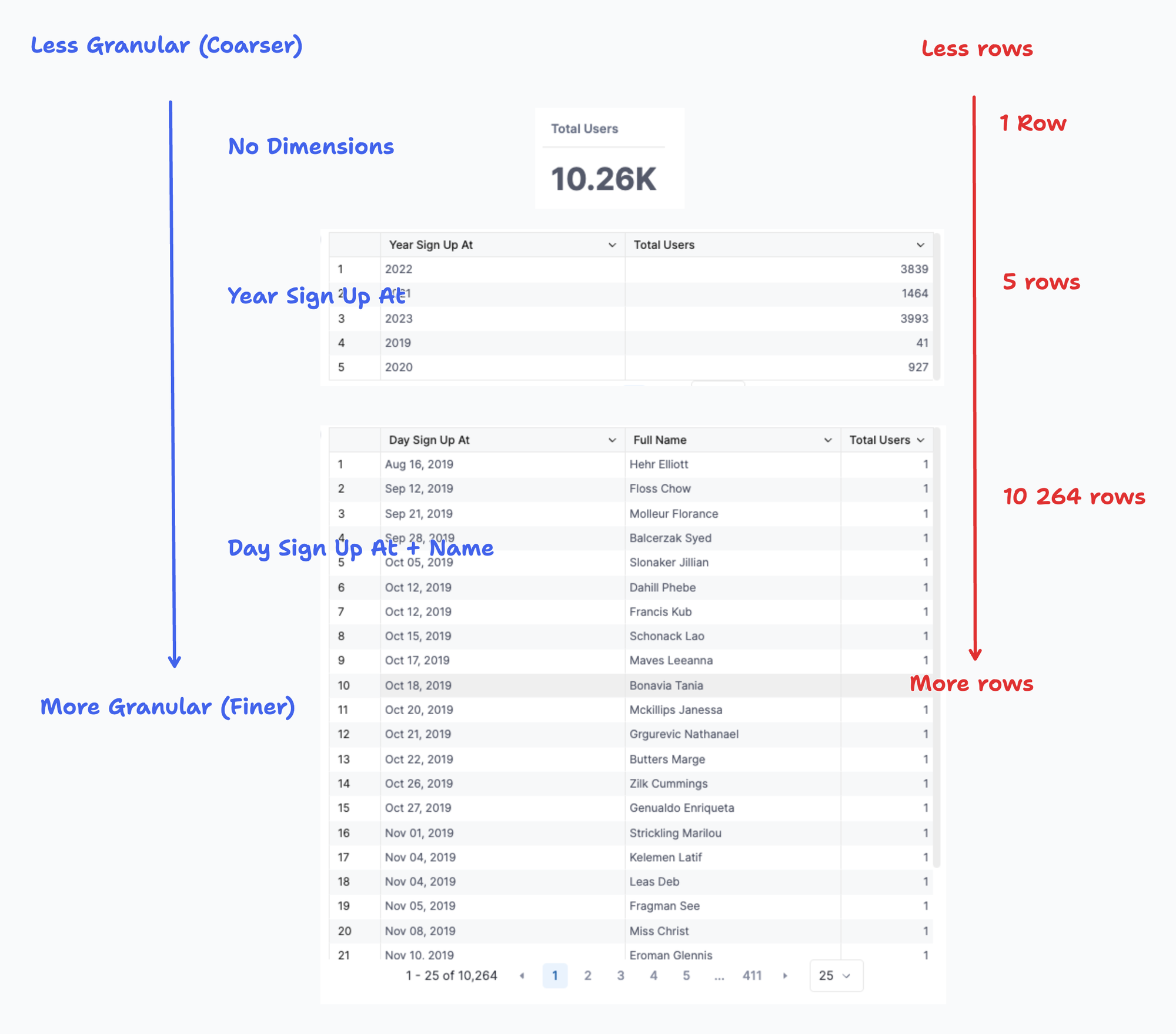
Dimensions are attributes of the model, and they give us the context to help us understand the meaning of the measures. For example, Total Users don't mean much as an isolated number

Using the Sign Up At dimension, we can break Total Numbers down into the month level and have more context to understand what it means

This gave us the context to understand:
- What is the increase this month?
- How is the increase compared to other months?
- Which month has the highest spike in Registered Users?
This type of analysis is called “slice-and-dice", meaning we chose an arbitrary set of dimensions to break a measure down to the Level of Detail defined by the dimensions.
What is a relationship
We have established that Data Model is a representation of a Business Entity, but Business Entities don't live in isolation. A User may have multiple Orders, an Order has multiple Order Items, and an Order Item is associated with a Product, etc. These relationships are crucial for analyzing data involving multiple entities

In Holistics, when models are connected by relationships, we essentially treat them as a single large model. What this means is that the models are joined dynamically at run-time, while retaining the correct relationship between data. This approach enables end-users to focus on the business logic and effortlessly explore data without worrying about how the data is combined
For example, since we have already created a relationship between Users and Orders, we can simply drag Full Name field from Users and Order ID from Orders into the exploration.

As a result, a unique Full Name is associated with multiple Order ID values, just like how the relationship is defined which follows the underlying business logic.
What is a dataset
In Holistics, a Dataset is a "container" holding several data models together so they can be explored together, and dictating which join path to be used in a particular analytics use case.
Fundamentally, a dataset is a compilation of models and their relationships. They form a graph representing how the model (business entities) are related through the established relationships. With a clear understanding of the role and functionality of models and relationships, we can see that dataset is just a way to organize them to solve some particular analytics use cases

From SQL to AQL
| SQL | AMQL | |
|---|---|---|
| Dataset | SQL doesn't inherently have a concept of datasets; data is queried from tables or views. | A container holding multiple data models together for cohesive exploration. It dictates join paths for specific analytics use cases. Fundamentally, a dataset compiles models and their relationships into a graph, representing how business entities are related. |
| Relationship | Based on common fields from more than one table, often involving primary and foreign keys. JOIN and ON operators are used to connect 2 related tables within the query | Based on common fields from more than one table. Relationships can be established within or separately from the datasets. Relationships enable users to treat connected models as a single large model and perform dynamic joining at runtime |
| Measure | An aggregation that is constructued from numerical fields and is included in SELECT clause | Any expression that can return a single scalar value and can change based on the context it is used in. |
| Dimension | A table field which is included in SELECT and GROUP BY clause | A dimension provides context to the measure, allowing it to be viewed from different angles and levels of detail |