Miscellaneous Functions
cast
cast(value, type)
cast('2021-01-01', 'date') // -> 2021-01-01
cast('2000.4', 'number') // -> 2000.4
cast('2000', 'int') // -> 2000
Input
-
value: The value to be casted -
type: Specifies the data type to cast to. Supported types include:datedatetimenumbertexttruefalseintorinteger(special cases of thenumbertype)
Note: The
intandintegertypes are treated asnumberbut will be cast to the integer type of the underlying database. Useintorintegerwhen you need to ensure the value is an integer, especially for functions that require integer input (e.g., mod).
Output
The value casted to the specified type.
is_at_level
is_at_level(dimension)
explore {
dimensions {
users.email
}
measures {
_email_active: is_at_level(users.email), // -> true
_name_active: is_at_level(users.name), // -> false
_nested_agg: unique(users.name) | select(
case(
when: is_at_level(users.name) // -> true
, then: count(users.id)
, else: 0
)
) | avg()
}
}
Description
This function returns true if the specified dimension is active in the Level of Detail (LoD) context, otherwise it returns false.
Return type
Truefalse
Sample Usages
The is_at_level function is used to conditionally modify the behavior of a measure based on the active dimensions in the Level of Detail (LoD) context. This function is typically paired with the case function to address scenarios such as calculating the Percent of Parent (Subtotal).
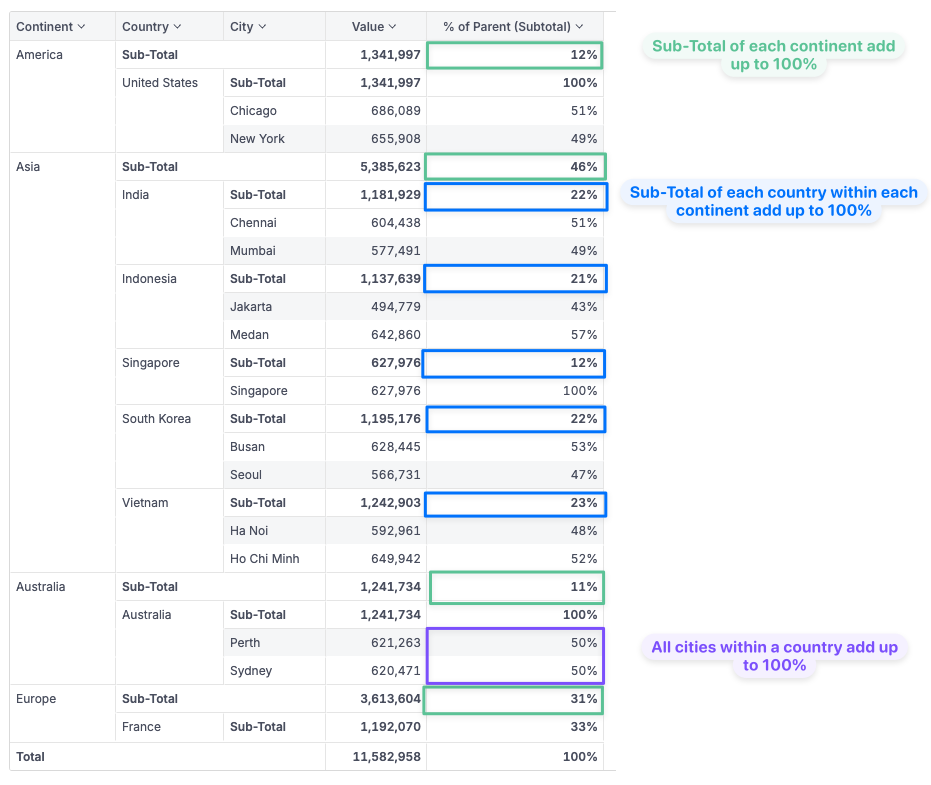
Example: Calculating Percentage Contributions in a Pivot Table
Imagine you have a Pivot Table with three hierarchical levels: Continent, Country, and City. You want to calculate the percentage of sales contribution at each level:
- City to Country
- Country to Continent
- Continent to Grand Total
To achieve this, the is_at_level function can identify the active dimension in the LoD context, allowing you to compute the correct percentage.
Here's how you can implement this logic:
case(
when: is_at_level(cities.name)
, then: sum(sales.amount) / (sum(sales.amount) | of_all(cities.name))
, when: is_at_level(countries.name)
, then: sum(sales.amount) / (sum(sales.amount) | of_all(countries.name))
, when: is_at_level(countries.continent)
, then: sum(sales.amount) / (sum(sales.amount) | of_all(countries.continent))
, else: 1
)
Explanation:
-
is_at_level(cities.name): Checks if the current dimension level isCity. If true, the calculation returns the percentage of sales for each city relative to the total sales of all cities. Sinceof_allis only applied tocities.name, this will be all cities within the same country. -
is_at_level(countries.name): Checks if the current dimension level isCountry. If true, the calculation returns the percentage of sales for each country relative to the total sales of all countries within the same continent. Note that we don't need to includecities.namein theof_allfunction because if it's active, it would've been caught by the first condition. -
is_at_level(countries.continent): Checks if the current dimension level isContinent. If true, the calculation returns the percentage of sales for each continent relative to the total sales of all continents. -
else: If none of the conditions are met, it simply returns 1. This is useful for the Grand Total row, where we don't need to calculate the percentage.
This approach allows you to dynamically adjust the measure based on the active dimension, ensuring accurate percentage calculations across different hierarchical levels.