AML Model Fields
A grasp of these concepts will help you understand this documentation better:
Dimension
Dimension represents a column in a table or a calculation. You can combine dimensions in the current model into a new dimension.
Parameter Definition
| Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
| label | Specifies how the dimension will appear in the Ready-to-explore Dataset |
| type | Specifies the data type you want to apply to the dimension. Possible values: 'text', 'number', 'date', 'datetime', 'truefalse' |
| description | Describes the semantic of the dimension |
| hidden | Hides dimension from the Exploration interface of Dataset and Report. This is not a Security Feature (Reason) |
| definition | Determines how the dimension will be calculated using SQL-based syntax or AQL syntax. |
| primary_key | Marks this dimension as the primary key of the model. This enables query optimization and supports Single Model Conditions in AQL. Only one dimension per model should have primary_key: true. |
SQL Definition of Dimension
The concept of definition: @sql {{ }};; refers to the way you specify how each dimension’s values should be retrieved or calculated based on SQL queries.
References: There are two ways to reference columns or dimensions within the SQL definition:
@sql {{ #SOURCE.column_name }};;: This references a column in the table connected to the current model.@sql {{ dimension_name }};;: This references another dimension defined within the same model.
Default Behavior: If the SQL definition for a dimension is not explicitly provided, Holistics assumes that there is a column in the underlying table with the same name as the dimension. This is useful for cases where the dimension's name matches a column name, and you want to use that column as the dimension's source.
Example of Dimension Syntax
Model orders {
type: 'table'
label: "Orders"
table_name: 'ecommerce.orders'
data_source_name: 'mydemodb'
description: "This is the AML Orders Model"
dimension id {
label: 'Order ID'
type: 'number'
primary_key: true // Mark as primary key for optimization and AQL features
definition: @sql {{ #SOURCE.id }};;
}
dimension status {
label: 'Status'
type: 'text'
//to reference the "status" column in the source table
definition: @sql {{ #SOURCE.status }};;
}
dimension created_at {
label: 'Created At'
type: 'datetime'
}
dimension created_at_year {
label: 'Created At Year'
type: 'number'
//to calculate the year from the "created_at" dimension
definition: @sql extract(year from{{ created_at }});;
}
}
Measure
Measure represents an aggregation operation in a model.
Parameter Definition
| Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
| label | Specifies how the measure will appear in the Ready-to-explore Dataset |
| type | Specifies the data type you want to apply to the dimension. Possible values: 'number', 'date', 'datetime' |
| description | Describes the semantic of the measure |
| hidden | Hides measure from the Exploration interface of Dataset and Report. This is not a Security Feature (Reason) |
| aggregation_type | Specify the aggregate function of the Measure. Supported functions: count, count distinct, sum, avg, max, min, max, median, stdev, stdevp, var, varp, custom (for when the expression in definition is not already an aggregation). This is optional. |
| definition | Determines how the measure will be calculated using SQL or AQL expressions. Learn more about the definition parameter below. |
SQL Definition of Measure
Forms: There are two primary forms that definition for measures can take:
-
Native Holistics Aggregation Type: Use aggregation type that Holistics natively supports such as sum, count, count distinct, avg, etc.. For example:
measure total_users {
label: 'Total Users'
type: 'number'
// The definition here is the inner expression of the aggregation
definition: @sql {{ user_id }};;
aggregation_type: 'count'
}When used in an explore, this measure will be treated as
COUNT({{ user_id }}) -
Custom Aggregation Form (
aggregation_type: 'custom'- this is the default when aggregation_type is not specified): The entire definition is used as the aggregation expression. This allows you to use aggregation functions from the source database that are not supported by Holistics (e.g. PERCENTILE_CONT from Redshift).measure percentile {
label: 'percentile'
type: 'number'
// must be valid aggregation expression that can be run in
// aggregation position of a query
definition: @sql percentile_cont(0.6) within group (order by {{ profit }});;
aggregation_type: 'custom'
}SELECT
col,
-- ...other group by columns
COUNT(*) -- The definition of custom aggregation must be an expression
-- that can be placed here
FROM orders
GROUP BY
1
-- , ...other group by columns
Additionally, you can write a custom measure with calculations between measures:
measure profit {
label: 'Profit'
type: 'number'
// must be valid aggregation expression that can be run in
// aggregation position of a query
definition: @sql {{ measure_revenue }} - {{ measure_cost }} + sum({{ dimension_discount }});;
aggregation_type: 'custom'
}
However, it's important to note that you cannot directly use dimensions without aggregation in a custom measure. For example:
measure profit {
label: 'Profit'
type: 'number'
// top level must be aggregated
definition: @sql {{ measure_revenue }} - {{ measure_cost }} + {{ dimension_discount }};;
aggregation_type: 'custom'
}
Example of Measure Syntax
Model users {
type: 'table'
label: "Users"
description: "This is the AML Users Model"
table_name: '"ecommerce"."users"'
data_source_name: 'demodb'
measure total_users {
label: 'Total Users'
type: 'number'
definition: @sql count({{#SOURCE.id}});;
aggregation_type: 'custom'
}
}
FAQs
How should I define aggregate functions for measures, and what are the important considerations?
- Choose between using
aggregation_typeparameter or using aggregation functions from the database withindefinition: @sql ;;parameter. It’s important to note that you should not define an aggregate function in both parameters.-
If you define an aggregate function using the
aggregation_type, thedefinition: @sql ;;parameter must not contain any aggregate functions.//What you should write:
measure measure_1 {
...
definition: @sql {{ user_id }};;
aggregation_type: 'count'
}
---------------------------
//What you should NOT write
measure measure_1 {
...
definition: @sql count{{ user_id }};;
aggregation_type: 'count'
} -
If you define the aggregate function within the
definition: @sql ;;parameter, make sure to set theaggregation_typetocustom.//What you should write:
measure measure_2 {
...
definition: @sql sum({{#SOURCE.id}});;
aggregation_type: 'custom'
}
-
Should I use the 'Hidden' Property in Dimension/Measure for Data Restriction Purposes?
The short answer is: you should not. The proper way to set up permission control is via Column-level Permission.
To explain, you can use the hidden: true property if you would like a dimension/measure to be accessible during development, but concealed from users in Reporting. This is achieved by hiding it within the Dimension/Measure Selection of the Dataset.
dimension id {
label: 'Id'
type: 'number'
hidden: true
definition: @sql {{ #SOURCE.id }};;
}
However, this method should not be applied as a means to restrict others from using these dimensions/measures in Reporting.
Despite being hidden, these dimensions/measures remain accessible through Dashboard Filters, Dataset Relationship, or AQL Expression.
Therefore, using the 'hidden' property primarily serves to declutter the Dimensions/Measures list in your Dataset.
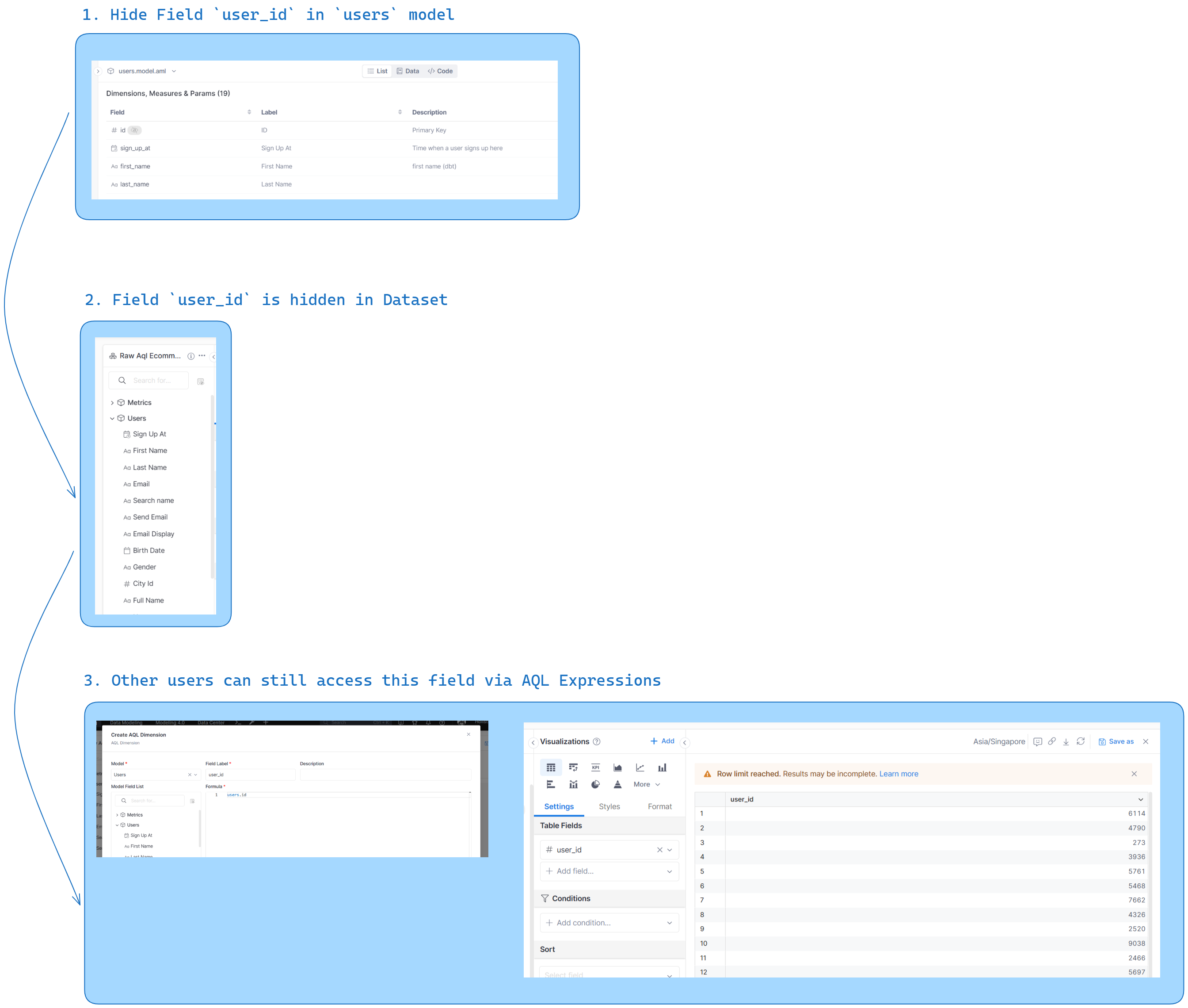
Therefore, if you want to restrict access control and disallow certain users to see certain Dimensions/Measures, you should use Column-level Permission instead.