Dimensions & Measures
Introduction
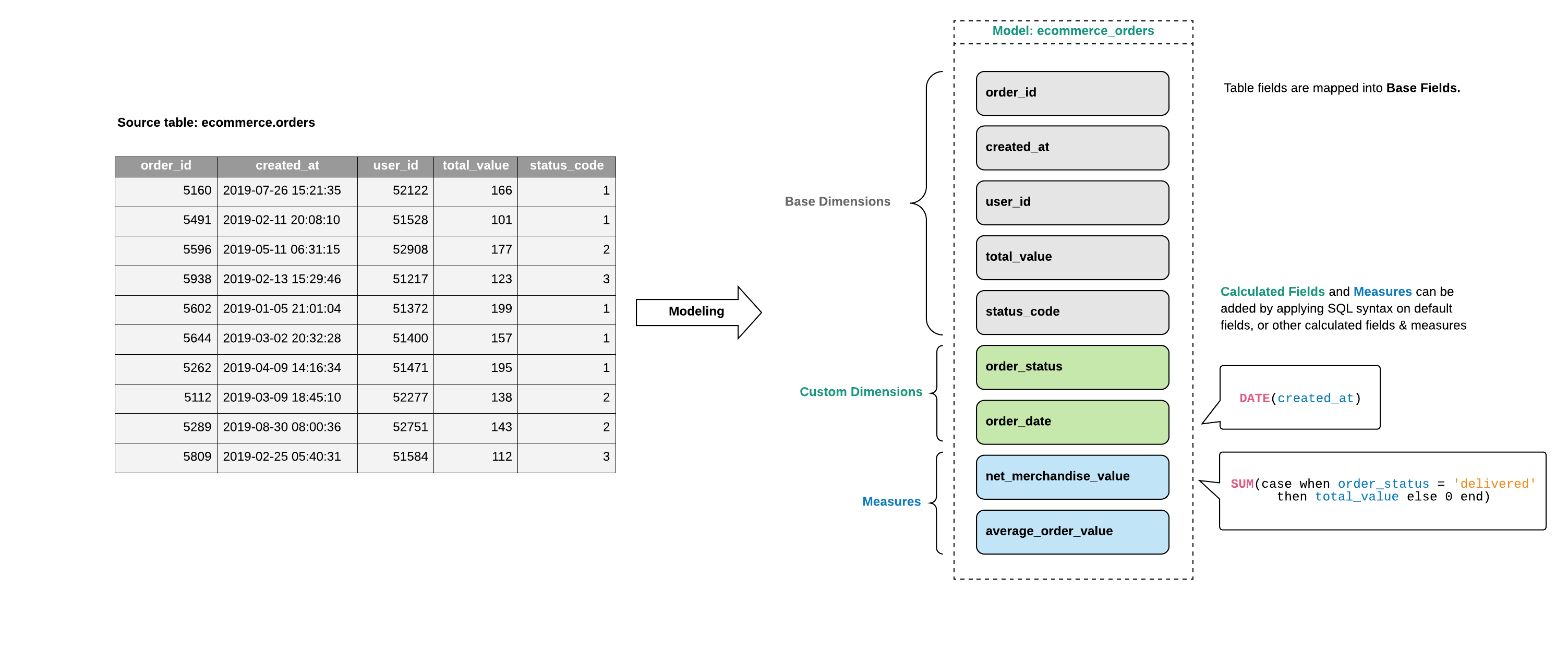
Each data model in Holistics has two types of field:
- Dimensions: These are non-aggregated fields in a model which can refer directly to the underlying table's columns, or is created using non-aggregate functions to transform other dimensions.
- Measures: These are created by using aggregate functions (SUM, COUNT, etc) and do not need to pre-define grouping dimension. Instead, the grouping will be added dynamically to the generated SQL when you combine Dimensions and Measures.
In the Business Intelligence (BI) world, the words “metric” and “measure” are often used interchangeably. Some BI tools use the term “metric”, while others use “measure”. However, in general, these terms are intended to convey the same meaning. This makes sense, as the word “metric” is derived from the Greek word “metron”, which translates to “a means of measure”.
In Holistics, we have both “metric” and “measure”, where “measure” is defined in a model, while “metric” is defined at the dataset level.
Dimensions
Adding new dimensions
When creating a new Table Model or Query Model using Holistics's GUI, the model will be initialized with some dimensions:
- In the case of Table Model, the dimensions represent the underlying columns of the table in the database
- In the case of Query Model, the dimensions represent the columns in the result of your SQL
When you add a new column to the underlying table or query, you can click Refresh Model to automatically create new dimensions for them.
Dimensions can also be added manually:
- Go to the model view UI, click Add -> Custom Dimension,
- Input field name and SQL formula.
- Click Create, and a new column named will be created
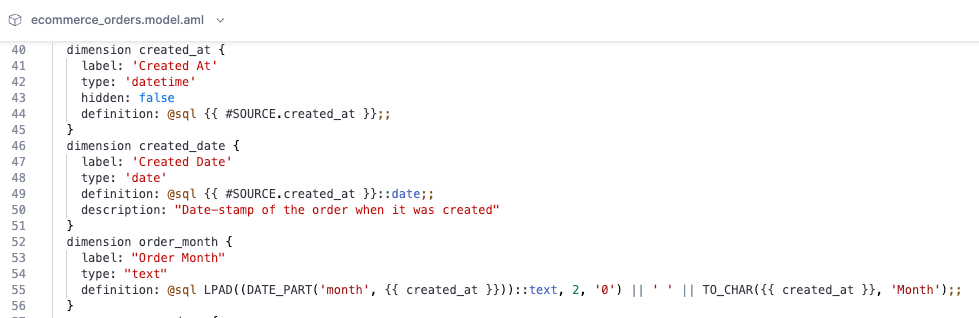
Below is the general form of the dimension's syntax. You can define dimension in either SQL or AQL. For more details on how to define dimension with AQL, please refer to single model dimension.
// SQL-based dimension
dimension dimension_name {
label: 'Dimension Label'
type: 'text' | 'number' | 'date' | 'datetime' | 'truefalse'
description: 'Field Description'
hidden: true|false
definition: @sql {{ dimension }};;
}
// AQL based dimension
dimension dimension_name {
label: 'Dimension Label'
type: 'text' | 'number' | 'date' | 'datetime' | 'truefalse'
description: 'Field Description'
hidden: true|false
definition: @aql aql_expression ;;
}
Please refer to AML Dimension Reference to learn more about all available parameters and their example usage.
When to manually add dimensions
Some common scenarios you might want to manually defined dimensions:
-
To discretize a field with continuous value:
CASE
WHEN {{ age }} > 30 then 'Older than 30 years old'
WHEN {{ age }} >= 18 and {{ age }} < 30 then '18 - 30 years old'
ELSE 'Under 10 years old'
END -
To combine values of two fields to create a new value (e.g
field_a + field_b){{ price }} - {{ discount }} -
To convert the data type of a field, such as converting an integer to a string:
CAST( {{ ranking }} AS STRING )
Measures
Adding new measures
Please refer to AML Measure Reference to learn more about all available parameters and their example usage.
To add a Measure in your Data Model:
- Go to the model view UI, click Add -> Measure,
- Input field name and SQL formula.
- Click Create, and a new measure will be created
You can define a measure using either SQL or AQL. For more details on how to use AQL to define measure, please refer to how to define metrics in AQL.
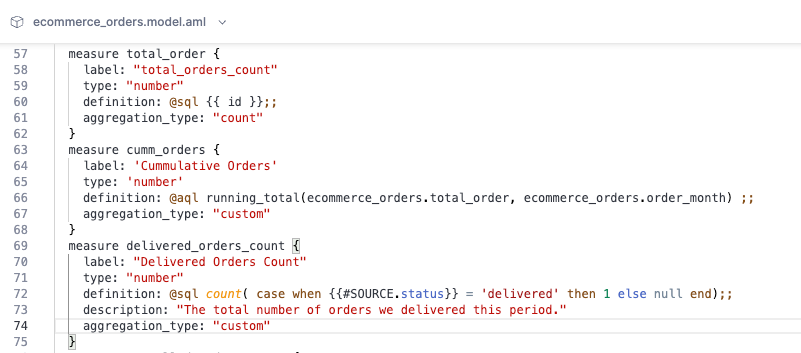
// you can define measure using SQL aggregation functions
measure measure_name {
label: 'Measure Name'
type: 'number' | 'date' | 'datetime'
definition: @sql count( {{ dimension }} );;
}
// alternatively, you can explicitly use `aggregation_type` to declare the aggregation
measure measure_name {
label: 'Measure Name'
type: 'number | date | datetime'
definition: @sql {{ dimension }};;
aggregation_type: 'count' | 'count distinct' | 'sum' | 'avg' | 'max' | 'min'
}
// you can also use AQL instead of SQL for measure definition
measure total_orders {
label: 'Total Orders'
type: 'number'
definition: @aql count(orders.id) ;;
}
// AQL measure allows more complex use case not available in SQL measure, such as percent
// of total use case below
measure total_orders_of_all_countries {
label: 'Total Orders of all Countries'
type: 'number'
definition: @aql orders.total_orders | of_all(countries) ;;
}
measure country_orders_pct {
label: 'Country Orders Pct'
type: 'number'
definition: @aql orders.total_orders * 1.0 / orders.total_orders_of_all_countries ;;
}
When to use measures
Measure is suitable when you have a complicated logic that the basic aggregation in the Exploration UI cannot satisfy. For example:
-
When your aggregation involves conditions:
// Count only delivered orders
SUM(CASE WHEN {{ status }} == 'delivered' then 1 else 0 end) -
When your aggregation involves multiple fields:
// Calculate profit
SUM( {{quantity}} * {{ price }} - {{ cost }})
Important Notes
- Manually defined dimensions and measures can only refer to fields within the same model. If you need to create a cross-model field, you can use a Query Model to join the related models and combine fields in the SQL. Alternatively, you can use Holistics's Cross-model Calculation feature with AQL metrics. More details about AQL metrics can be found in creating metrics in datasets.
- The value of manually defined dimensions and measures are calculated at run time, and when you use Persistence feature, they are not recorded to your database.
Advanced Use Case
If you need to set up Dynamic Dimensions and Measures Selection in your dashboard, please refer to the following documentation: