Build Relationships
A grasp of these concepts will help you understand this documentation better:
Once you've created your data models, you can specify how they should be linked together by setting up Relationships.
This step is needed for Holistics to build the right SQL query when you combine fields from different models to create a report.
Creating Relationship
Please refer to AML Relationship to learn more about all available parameters and their example usage.
In Holistics 4.0, a relationship can be defined within a dataset or as separate relationship files. You can either use the interactive UI to create a relationship, or define them programatically using AML syntax.
Define Relationship inside Dataset (using Interactive UI)
This option is only available inside a Dataset
The generated AML syntax will be like below:
Dataset ecommerce {
...
models: [
orders,
users,
order_items,
countries,
merchants,
products,
cities,
param_model
]
relationships: [
relationship(order_items.order_id > orders.id, true),
relationship(order_items.product_id > products.id, true),
relationship(products.merchant_id > merchants.id, true),
relationship(merchants.city_id > cities.id, false),
relationship(orders.user_id > users.id, true),
relationship(users.city_id > cities.id, true),
relationship(cities.country_code > countries.code, true)
]
}
For more details, please refer to Relationship in Dataset
Define Relationship in a separated file (using AML syntax)
You can define the relationship in a model file or define the relationship as a separate file.
//Relationship defined in relationship file: relationships.aml
Relationship order_items_products {
type: 'many_to_one'
from: FieldRef {
model: 'order_items'
field: 'product_id'
}
to: FieldRef {
model: 'products'
field: 'id'
}
}
And then, when you want to add that relationship to the Dataset, simply reference the relationship name and indicate whether you want it enabled or disabled.
Dataset ecommerce {
...
models: [order_items, products]
relationships: [
relationship(order_items_products, true),
]
}
Learn more about Relationship AML syntax by visiting AML Relationship.
Automatic Relationship Creation
In some databases where foreign key constraints are already implemented, Holistics will automatically detect these constraints and turn them into relationships.
Currently, this feature is available for the following databases:
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Redshift
Relationship on Composite Keys
There are cases where models must be joined on two keys. For example, last year's sales aggregation by cities vs. this year's sales aggregation by cities:

The intended query is:
select
ty.city
, ty.month
, sales_this_year
, sales_last_year
from this_year ty
join last_year ly
on ty.city = ly.city and ty.month = ly.month -- using two keys
In Holistics, to replicate this behavior, you can concatenate the individual keys to create compound keys (using Custom Dimensions), and add a relationship on these fields.

With this approach, the generated query will be:
select
ty.city
, ty.month
, sales_this_year
, sales_last_year
from this_year ty
join last_year ly
on concat(ty.city, ty.month) = concat(ly.city, ly.month) -- using one compound key
Handling many-to-many (n-n) relationship
It is not possible to specify a many-to-many (n - n) relationship directly. To join models with n - n relationships, you will need a junction model, which you can create with a Query Model, so that the relationship is interpreted as 1 - n - 1.
Consider the following case where you have two models: products and merchants. Products can have multiple merchants, and a merchant can provide many products.

To join these two models, you will need a products_merchants junction model:

After that, you are good to explore datasets with those 3 data models.
Common got-chas
Fan-out issues
When you set relationships between models (many-to-one or one-to-one ), we assume that the fields at the "one" end is already unique.
If the field is not unique, when you drag in fields from those two models, a fan-out will happen. The result set will be a Cartesian product of the two models and may "explode" into millions of rows.
This would result in the fan-out error in the Data Exploration window.
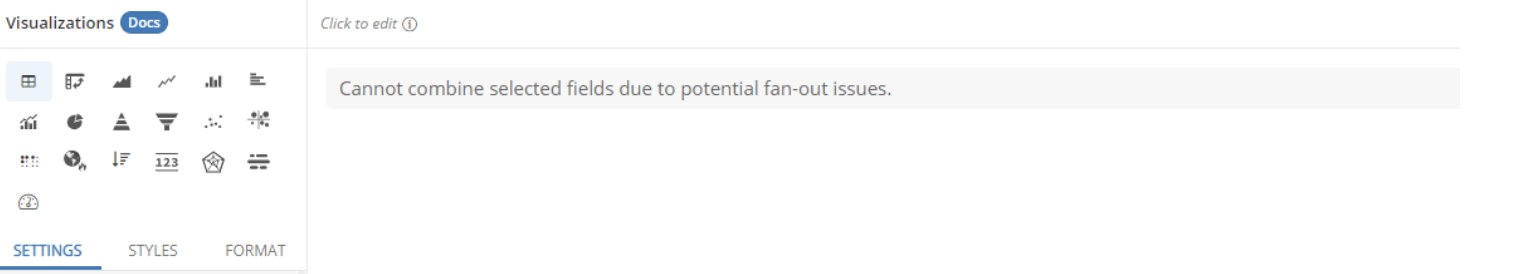
Visit Cannot combine fields due to fan-out issues? to learn more about this error and how to troubleshoot it.