Tags
Introduction
Tags help you efficiently categorize analytics content, allowing users to quickly discover related items through meaningful categories and labels.

High-level concept
Tags are a type of object metadata that helps organize and categorize your analytics content. Tags can be assigned to dashboards, datasets, and data models.
Key characteristics:
- Unique name: Each tag name must be unique and is case insensitive. Renaming a tag to an existing name will merge these two tags.
- Nested structure: You can create nested tags up to one level deep (e.g.,
status/done). - Enrich details: You can make your tags more meaningful and visually distinctive by adding descriptions and colors.
How-to
Create tags
Admin can follow the tutorial here to automatically set up the organization tagging system.
You can create tags in two ways:
-
Centralized in
tags.aml: All tags are centralized in thetags.amlfile, located in Development > settings folder. Using the Code or Visual editor, you can:- Create, view, edit (name, description, and color), and delete tags
- Manage all data models, datasets, and dashboards associated with a specific tag
-
Directly on objects: Create tag by adding them directly to objects without pre-defining them.
Add tags to an item
Tags can be assigned to (or removed from) items in both environments:
- In Development: You can either assign existing tags to an item, or create a new one.
- In Reporting: You can only assign existing tags to an item.
Any user with edit permissions on a specific item can assign and remove tags from that item.
Supported objects
- Data model
- Dataset
- Dashboard
- Widget (to be supported)
- Field (to be supported)
Syntax
tags.aml file: This file centralized the as-code definition of all tags.
// Create a new tag in tags.aml
Tag {
name: 'Sales'
description: 'Relates to Sales team.' // Optional
color: '#C53BFF7' // Optional
}
Tag {
name: 'status/WIP' // Nested tag is supported
description: "Don't use these items." // Use double quote if the content includes quote marks.
}
Object’s file (e.g., dashboard.page.aml): In each tagged object's file, tags are reference as-code.
// Add a tag to a data model
@tag('marketing', 'high-level metrics')
Model facebook_ads {
type: 'table'
label: 'Facebook Ads Data'
description: ''
data_source_name: ''
}
// Add a tag to a dashboard
@tag('status/WIP', 'verified')
Dashboard ecommerce {
block v1: VizBlock {
}
}
Special cases
Ad hoc tags
Ad hoc tags are tags created directly on an item, using the Code Editor. These tags are visible in the Visual Editor but not available in the code file of the tags.aml file. They display with a dashed border to visually distinguish them from normal tags.
Once you add metadata (color, description) to these tags, they will be auto-added to tags.aml and become a normal tag.
Merging tags
You can merge two existing tags by renaming one tag to match another in the tags.aml file. This is useful when you have duplicate or similar tags that should be consolidated.
After merging:
- All items previously tagged with tag A are auto-reassigned to tag B
- The merged tag retains all metadata and characteristics of the original tag B
- Tag A is removed from the system
For example, if you rename “Marketing Dept” to “Marketing,” all dashboards and datasets tagged with “Marketing Dept” will automatically be retagged as “Marketing".

Tags of extended items
When you extend an item from a master item using AML Extend, the extended item automatically inherits all tags from its master. However, if you add new tags directly to the extended item using code, these new tags will override the inherited tags.
For example, imagine you have a master dashboard called “Original Ecommerce” with two tags status/WIP and high-level metrics .

When you create an extended dashboard named “Extend Ecommerce” from “Original Ecommerce”, it will initially inherit these two tags:

But, if you then add a new tag, dept/Sales, directly to the “Extend Ecommerce” dashboard, it will only have the dept/Sales tag. The inherited tags (status/WIP and high-level metrics) will be replaced.

FAQs
1. We’re on version 3.0. How can we use Tags features?
Tagging System is available exclusively on Holistics version 4.0. Please ensure you are using this version.
If not, you can migrate your Holistics instance to version 4.0.
2. How to set up your tagging system?
Option 1: Auto setup (Only available to admins, and tenants without the tags.aml file)
Admins can automatically set up the organization tagging system with a default tag list and configure the two special tags (endorse/archive).
Option 2: Manual setup (Available to analysts and admins)
- Go to Development, find your
tags.amlfile in settings folder or create it yourself - Copy our recommended list of tags into your
tags.amlfile - Publish to save your changes
- Preview the list
- Get the code
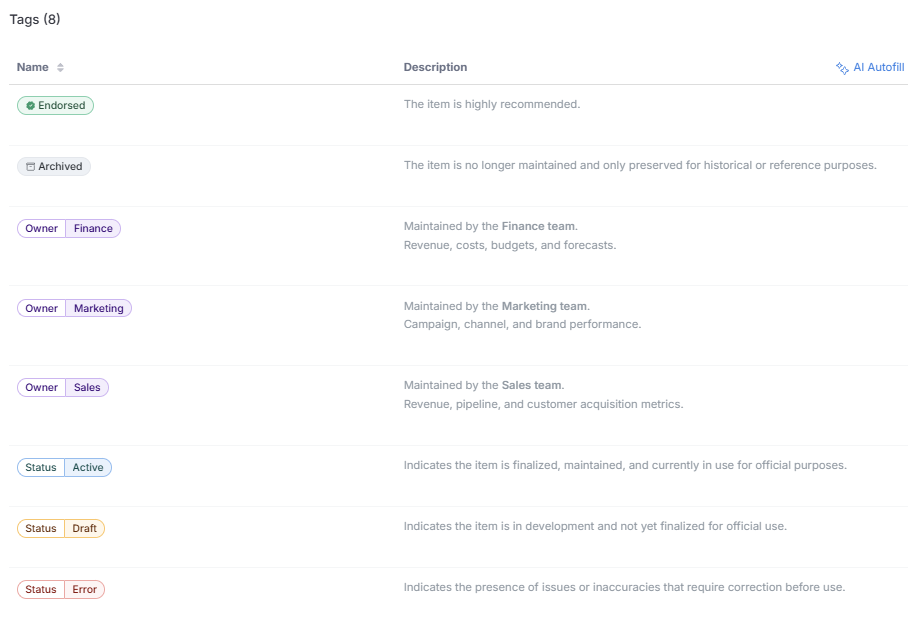
// #############################################################
// 📘 TAGGING SYSTEM OVERVIEW
//
// This section defines a reusable tagging system to help BI teams manage:
// - 🎯 System: Special tags with automated behaviors (endorsement & archival)
// - 📊 Status: Track content maturity and maintenance needs
// - 🧑💼 Owner: Identify which team maintains this content
//
// 🎯 PURPOSE:
// Tags help BI teams communicate quality, lifecycle, and ownership directly
// inside the reporting tool. It's part of a best practice for dashboard governance.
//
// 🛠️ SETUP INSTRUCTIONS:
// For more information, visit our public docs:
// - https://docs.holistics.io/docs/find-organize/tags
// - https://docs.holistics.io/docs/find-organize/content-endorsement
// - https://docs.holistics.io/docs/find-organize/archive
//
// #############################################################
// ---------------------
// 🎯 SYSTEM TAGS
// Special tags with automated platform behaviors
// ---------------------
Tag {
name: 'Endorsed'
color: '#00ff00'
description: 'The item is highly recommended.'
}
Tag {
name: 'Archived'
color: '#808080'
description: 'The item is no longer maintained and only preserved for historical or reference purposes.'
}
// ---------------------
// 📊 STATUS TAGS
// Track content maturity and maintenance needs
// ---------------------
Tag {
name: 'Status/Active'
color: '#00ffff'
description: 'Indicates the item is finalized, maintained, and currently in use for official purposes.'
}
Tag {
name: 'Status/Draft'
color: '#ffa500'
description: 'Indicates the item is in development and not yet finalized for official use.'
}
Tag {
name: 'Status/Error'
color: '#ff0000'
description: 'Indicates the presence of issues or inaccuracies that require correction before use.'
}
// ---------------------
// 🧑💼 OWNER TAGS
// Identify which team or department owns and maintains this content
// ---------------------
Tag {
name: 'Owner/Sales'
color: '#800080'
description: @md Maintained by the **Sales team**.
Revenue, pipeline, and customer acquisition metrics.;;
}
Tag {
name: 'Owner/Marketing'
color: '#800080'
description: @md Maintained by the **Marketing team**.
Campaign, channel, and brand performance.;;
}
Tag {
name: 'Owner/Finance'
color: '#800080'
description: @md Maintained by the **Finance team**.
Revenue, costs, budgets, and forecasts.;;
}